Gastric and colorectal cancers (GC and CRC) are often resistant to standard treatments like chemo and radiotherapy. However, combining dendritic cell immunotherapy with cytokine-induced killer cells (DC/CIK) has shown promise in reducing the risk of post-operative disease progression and increasing overall survival for GC and CRC patients. This approach can effectively control tumor growth after surgery, offering hope for better outcomes. Though more research is needed before widespread adoption, this treatment holds great potential for improving survival rates in cancer patients who are not eligible for conventional therapies. The most common side effect observed in patients was fever, which was manageable and not severe.
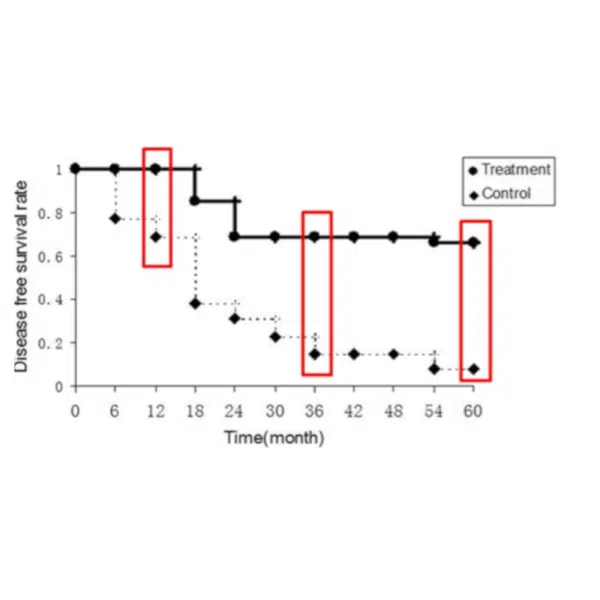
Gastric and colorectal cancers (GC and CRC) are resistant to chemo- and/or radiotherapy Dendiritc Cell immunotherapy combined with cytokine-induced killer (CIK) reduced the risk of post-operative disease progression with an increased overall survival. These results demonstrate that in addition to chemo- and/or radiotherapy, DC/CIK immunotherapy is a potential effective approach in the control of tumor growth for post-operative GC and CRC patients.
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death in people worldwide. Autologous tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cell immunotherapy with cytokine-induced killer cells has shown great potential to improve survival rates for gastric and colorectal cancer patients, but more communication needs to be done before it can become a mainstream treatment option. This article will discuss how this treatment works, what benefits it offers, and why more research is needed before it can be used as a mainstream cancer treatment.
Many cancer patients are not eligible for surgery or radiation therapy due to increased risk factors such as old age, poor health, and other medical conditions. These people often do not survive past five years after diagnosis. One treatment that has shown promise in improving these survival rates is DCT (dendritic cell therapy). The DCT involves the production of autologous tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells which are then injected into the patient’s body where they stimulate an immune response against the cancer cells. This type of DCT has been used successfully with gastric and colorectal cancers, showing significant improvement in survival rates.
The most common adverse effect observed in all patients receiving DC/CIK therapy was fever, which occurred in 9 of 27 treated patients (33%) in the range of 37.5–40uC. All patients recovered spontaneously or after antipyretic treatment with non- steroid medicine. No other significant complications accompany- ing cell-based immunotherapy were observed.
Autologous tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cell immunotherapy with cytokine-induced killer cells improves survival in gastric and colorectal cancer patients. Recent studies have shown that this type of treatment can increase the percentage of long term survivors by up to 80%. The therapy is used for people who are not candidates for surgery or conventional treatments, due to their advanced stages of cancer. This therapy has been successful in treating some tumors that were previously considered incurable.
© 2025 Immucura. All Rights Reserved
Caricamento modulo: attendere prego…
Caricamento modulo: attendere prego…
Loading form… Please wait…